Disposable Clients in libtaskotron¶
Limiting task execution to a persistent or local machine has the unfortunate side effect of limiting the things which can be done inside tasks. For example, a task which can corrupt the filesystem where it’s running can’t really work if the client system is expected to survive for long periods of time.
To address this, libtaskotron has a concept of disposable clients - single use virtual machines which are spun up for the sole purpose of running a task, extracting interesting output and destroying that virtual machine upon completion.
New Terms and Definitions¶
Using disposable clients introduces a few new terms:
- Overlord
- Orchestrates task execution, making the determination whether to run a given task locally or using a minion.
- Minion
- In the non-local case, execution is delegated to a minion which prepares the execution environment and spawns an Executor to do the low level work.
- Executor
- Coordinates and executes the individual steps of a formula.
Possible Task Execution Processes¶
The exact process used to execute a task depends on the options specified at execution time. The default in non-production environments is to use local execution.
Local Execution of Tasks¶
Local execution is the simplest of the processes used by libtaskotron. The task is processed on the local machine using the user which was used to start execution.
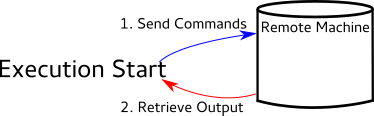
Task Execution via Remote Connection¶
libtaskotron is also capable of using a persistent virtual machine for executing tasks. This is mostly meant for libtaskotron and task development so that there isn’t a constant overhead of starting and configuring single-use virtual machines.
Task Execution using Disposable Clients¶
Disposable clients involve spawning a virtual machine, configuring it to spec, using it to execute a task before the info we’re interested in is extracted and the VM is destroyed.
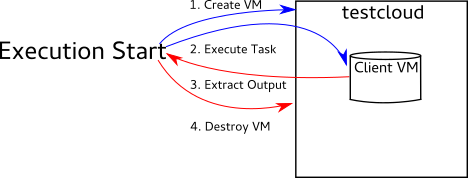
The specific process is:
- Start Execution
- Spawn VM using testcloud
- Configure VM per formula specifications
- Execute task on spawned VM
- Extract desired information
- Destroy spawned VM
While this is used in production, it’s not usually the most efficient method for executing tasks during development with the exception of testing the entire process before completion.
What Can I Do with Disposable Clients?¶
There is little that you can’t do with disposable clients - they effectively enable root access on a VM that you can do pretty much whatever you want to that VM. It might be a little difficult to extract data if you completely destroy the VM to the point where it isn’t functioning anymore but it won’t affect other tasks.
What is Coming for Disposable Clients?¶
At the time of this writing, disposable clients are a new feature for libtaskotron and we have a lot more planned including:
- Specifying a fedora version to run against
- Specifying a non-standard image to run against